In the vast and complex landscape of business strategy, the 80/20 Rule, also known as the Pareto Principle, stands as a cardinal rule for driving sustainable growth and optimizing profitability. First identified by Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, this principle asserts that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. In business terms, this often translates to 80% of revenue being generated by 20% of products, customers, or efforts (Abyad, 2020). Harnessing this power law demands precision and focus – qualities essential for firms navigating competitive markets and resource constraints.
The Pitfalls of Diffused Resource Allocation
Many businesses err by allocating resources – whether financial, human, or operational – across their entire product or service portfolio without sufficient prioritization. This scattergun approach dilutes brand equity, which embodies the perceived value of a brand in the minds of consumers, thereby weakening market positioning and identity (Qiao et al., 2022). Moreover, it introduces operational inefficiencies by complicating inventory management, marketing initiatives, and distribution logistics. For example, splitting your marketing budget equally across all stock-keeping units (SKUs) usually leads to weaker returns and a confusing brand message.

Identifying High-Margin Drivers as the Crux of Strategic Focus
Chammassian (2025) posits that the essence of applying the 80/20 Rule is to rigorously identify 20% of products or customers that generate most of your profits, focusing on the ones with the highest margins. These are offerings where revenue substantially exceeds the direct cost of goods sold, fueling financial health and competitive advantage. Prioritizing these drivers enables targeted investment of marketing budgets, enhancement of distribution channels, and tailored promotional efforts.
Systematic Data-Driven Implementation
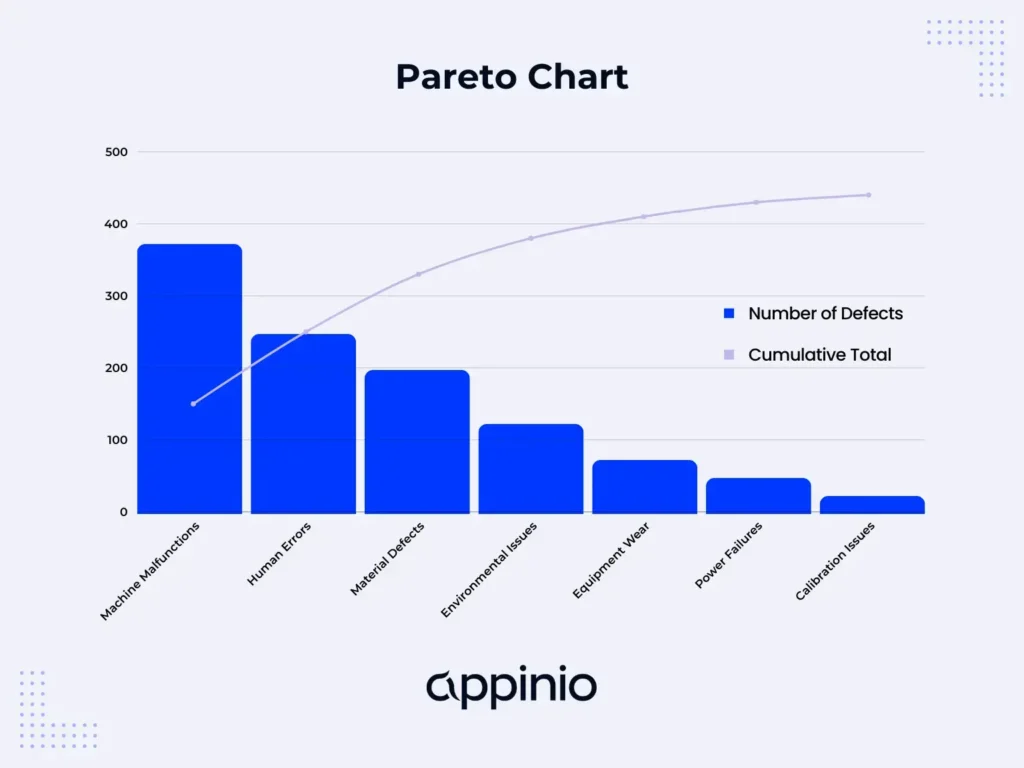
Successful application of the 80/20 Rule requires a systematic, data-driven approach that begins with clearly defining success metrics, such as revenue growth, market share, or customer retention, to ensure meaningful prioritization. Reliable data collection, including customer feedback, sales figures, and operational insights, forms the backbone of this strategy, enabling comprehensive analysis (Bajaj et al., 2018). Using statistical tools, businesses then segment their offerings, customers, or channels to identify the vital few contributors—typically the top 20% that generate around 80% of results. Finally, resources such as marketing budgets, manpower, and promotional efforts are strategically concentrated on these high-impact areas, while less critical segments receive proportionally less attention. This focused allocation drives efficiency, maximizes return on investment, and strengthens competitive positioning by aligning efforts with the most profitable opportunities.
Marketing Applications and Strategic ROI Enhancement
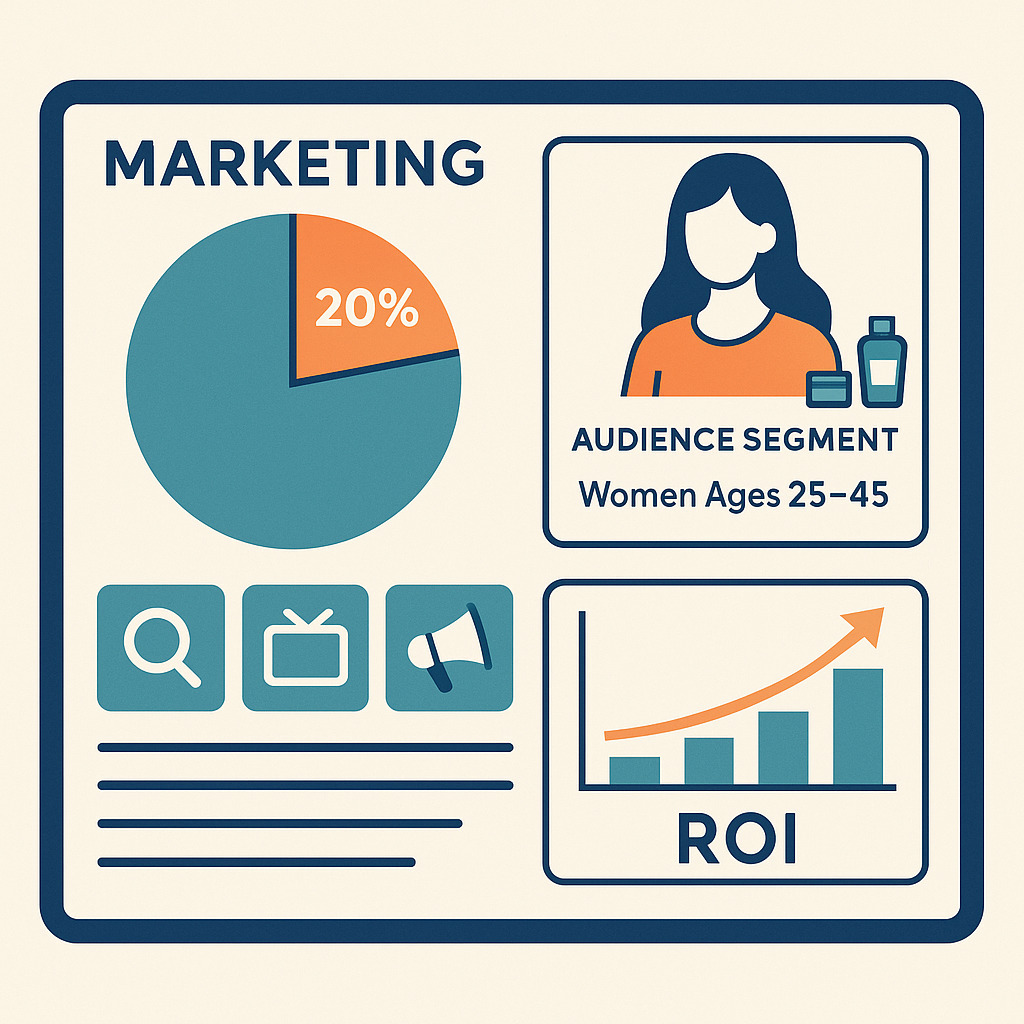
The 80/20 Rule in marketing emphasizes that a small subset of customers, products, and channels generate the majority of your revenue, and understanding this allows for more efficient resource allocation. For instance, if a store identifies that its top 20% of customers are primarily women aged 25 to 45 who purchase premium skincare products, it can then tailor marketing efforts specifically toward this demographic—using targeted offers, personalized messaging, and optimizing advertising spend on the channels that are most effective. Mou (2024) notes that by focusing spending on these high-impact segments and personalized channels, businesses not only boost sales and customer loyalty but also significantly reduce wasteful advertising expenditures. This strategic focus creates a more efficient marketing ecosystem, leveraging data insights to maximize return on investment (ROI) and refine overall business performance.
Mastering Business Complexity Through Focused Precision
In retrospect, the 80/20 Rule is not merely a heuristic but a strategic imperative for managing complexity and accelerating business performance. Businesses that embrace this principle move beyond superficial activity to unearth the critical drivers of success, catalyzing higher profitability, stronger brand equity, and streamlined operations. The adage, “If you’re marketing everything, you’re marketing nothing,” encapsulates the fundamental lesson: success demands judicious focus on the few that matter most.
By deploying data-driven insights and concentrating resources on high-impact areas, firms can unlock disproportionate value and thrive amid competitive pressures. In today’s dynamic markets, precision is not just advantageous—it is essential.
References
- Abyad, A. (2020). The pareto principle: applying the 80/20 rule to your business. Middle East Journal of, 15(1), 6-9.
- Bajaj, S., Garg, R., & Sethi, M. (2018). Total quality management: a critical literature review using Pareto analysis. International journal of productivity and performance management, 67(1), 128-154.
- Chammassian, R. G. (2025). Costs and Entrepreneurial Startup Lifecycles—Mid-to-Late Stages. In Costs, Value, and the Entrepreneurial Venture Journey: Developing Value-Driven Ventures (pp. 119-190). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Mou, A. J. (2024). MARKETING CAPSTONE INSIGHTS: LEVERAGING MULTI-CHANNEL STRATEGIES FOR MAXIMUM DIGITAL CONVERSION AND ROI. Review of Applied Science and Technology, 3(04), 01-28.
- Qiao, Y., Yin, X., & Xing, G. (2022). Impact of perceived product value on customer-based brand equity: Marx’s theory–value-based perspective. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 931064.